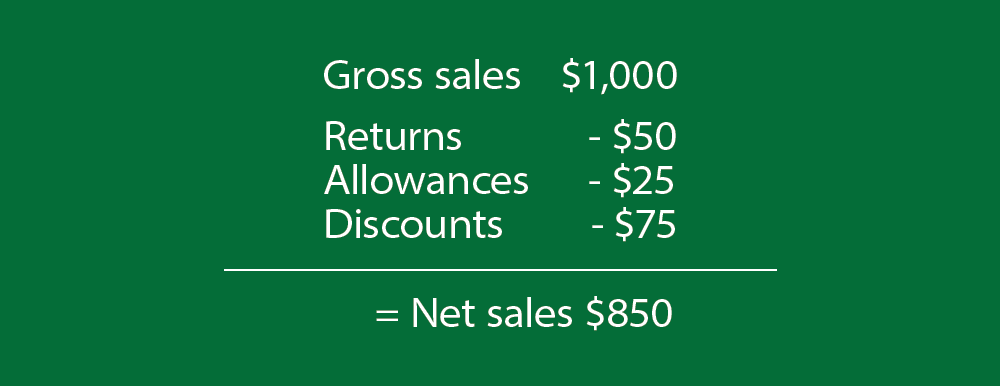Understanding the difference between the two, how they are calculated, and how they can be used to improve your business can make a big difference in your bottom line.
While gross values provide an overview of a company’s performance, net amounts offer a more accurate reflection of revenue. They are two important metrics for measuring your success.
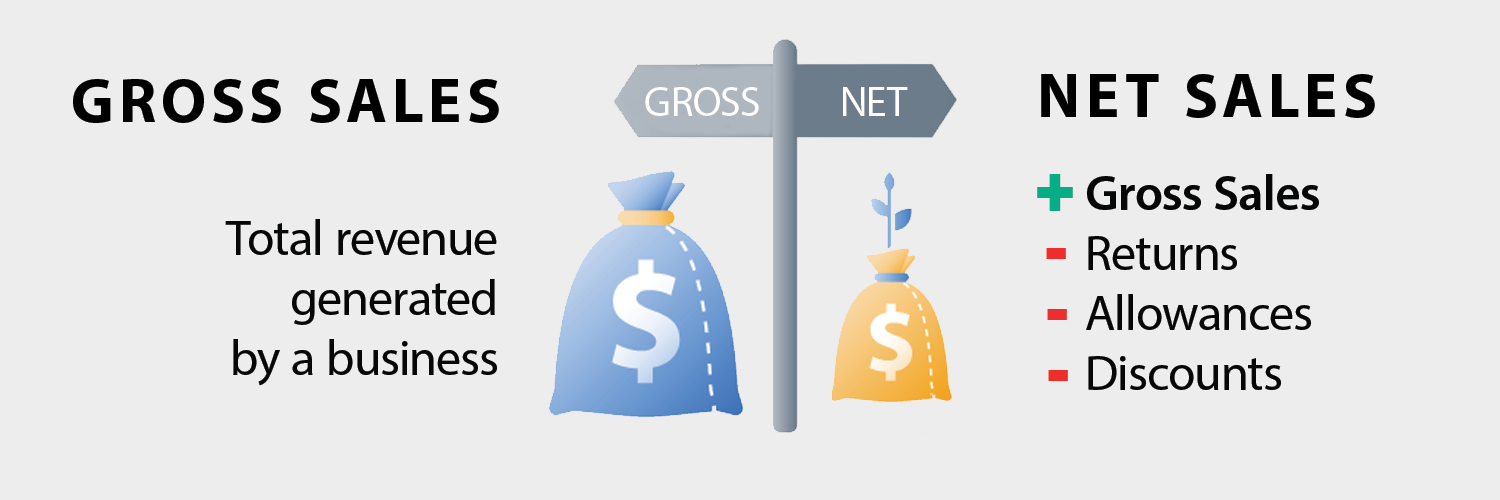
What are Gross and Net Sales?
Gross Sales refer to the total revenue generated from the sale of goods or services. They include all transactions, regardless of whether they were made at full price, at a discount, or as part of a promotion. In other words, they are a measure of the overall performance of a business and are typically reported on a company’s income statement.
On the other hand, Net Sales refer to the revenue generated after deducting any returns, allowances, or discounts given to customers. These are often considered to be a more accurate reflection of a company’s performance, as they account for factors that can affect revenue, such as customer returns, damaged goods, or discounts.
How to Calculate Gross Sales
Calculating this amount is relatively straightforward. Simply add up all of the revenue generated from your deals during a specific period of time, such as a day, week, or month. This can be done using transaction records, cash register receipts, or other documentation.
Formula:
Gross Sales = Number of units x Unit price
Example:
A company sells 100 widgets for $10 each during the month of January. The gross total for January is $1,000 (100 widgets x $10).
How to Calculate Net Sales
Calculating the net is slightly more complicated, as it requires deducting any returns, partial refunds, allowances, or discounts.
Formula:
Net Sales = Gross Sales - Returns - Allowances - Discounts
Returns refer to goods that were returned to the business by customers. Allowances refer to discounts that were given to customers for damaged or defective goods. Discounts refer to any price reductions that were offered to customers, such as sales promotions or bulk discounts.
Example:
A company had transactions of $1,000 in May, but also had $50 in returns, $25 in allowances, and $75 in discounts. The net sales for May would be $850 ($1,000 – $50 – $25 – $75).
Benefits of Knowing Gross and Net
In short, they can provide valuable insights into the performance of your organization. Here are a few benefits of understanding these metrics:
1. Understanding Revenue Trends
By tracking net sales over time, you can identify trends in your business’s revenue.
Are your deals increasing or decreasing? Are certain products or services selling better than others?
This information can help you make informed decisions about your future, such as whether to invest in new products or services.
2. Identifying Areas for Improvement
If you notice that your net values are consistently lower than your gross values, it may be a sign that there are issues with your business’s operations.
For example, you may be offering too many discounts or not managing returns effectively. By identifying these areas for improvement, you can take steps to address them and increase your bottom line.
3. Comparing Performance to Industry Benchmarks
Knowing your gross and net values can also help you compare your performance to industry benchmarks.
This can provide valuable insights into how your company is performing relative to your competitors and help you identify areas where you may need to improve your processes or marketing strategies.
4. Making Informed Decisions
By having a clear understanding of your gross and net sales, you can make informed decisions about your business.
For example, you may choose to invest in marketing campaigns to boost your gross transactions, or you may decide to tighten your returns policy to reduce the number of returns and allowances affecting net sales.
The impact of cost of goods (COGS)
COGS is the cost of producing or acquiring the products or services that a business sells. It is subtracted from sales to obtain the gross profit, which is then used to calculate the net profit.
Understanding the relationship with COGS can provide important insights into a business’s profitability.
Gross Profit = Revenue − Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Sales returns and allowances
Both returns and allowances can have a significant impact on net sales. Tracking these metrics can help businesses identify patterns and trends in customer behavior, such as whether certain products or services are more likely to be returned.
By addressing the underlying causes of returns and allowances, businesses can improve customer satisfaction and reduce the negative impact on their net sales.
Promotional activities
Sales Promotions such as discounts, coupons, and free shipping can have a significant impact on sales, if they are not managed effectively.
For example, if a company offers a discount that is too steep, it may erode its profit margin and reduce its net sales.
On the other hand, if a business offers a well-designed promotion that encourages customers to buy more, it may increase its gross sales while also improving its net sales.
The role of taxes
Taxes can have a significant impact. Sales tax, for example, is usually added to the price of goods or services and is included in gross sales.
However, businesses can often claim back the tax they paid on their purchases when they file their tax returns.
Understanding how taxes affect results can help businesses plan for their tax liabilities and optimize their tax strategies.
Revenue growth
Net values are an important metric for measuring revenue growth, which is the rate at which the net income is increasing over time.
Also, by tracking gross sales over time and comparing them to industry benchmarks, you can identify opportunities for growth and adjust your strategies accordingly.
Final thoughts
By understanding these metrics and how to calculate them, businesses can gain valuable insights into their revenue trends and identify areas for improvement. Ultimately, this information can help you make informed decisions to increase your bottom line and grow your business.